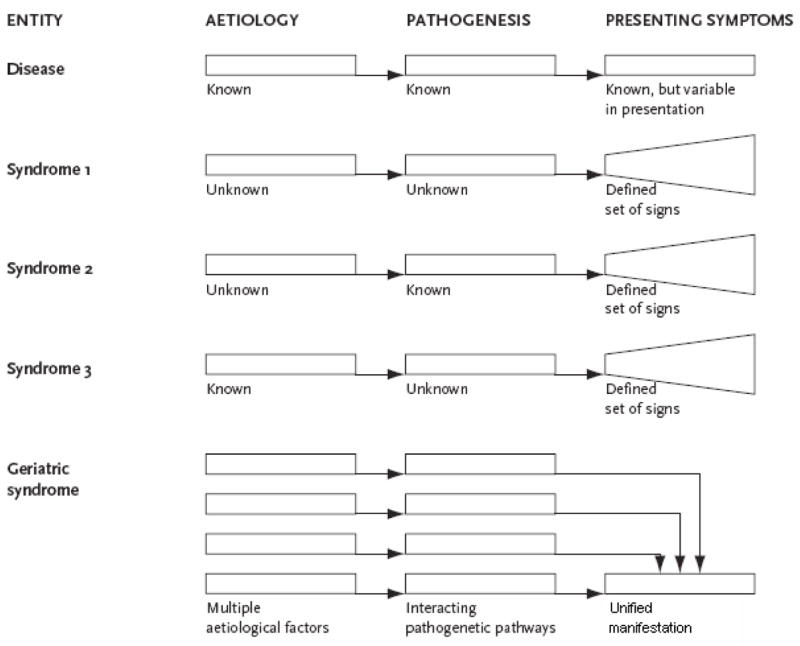
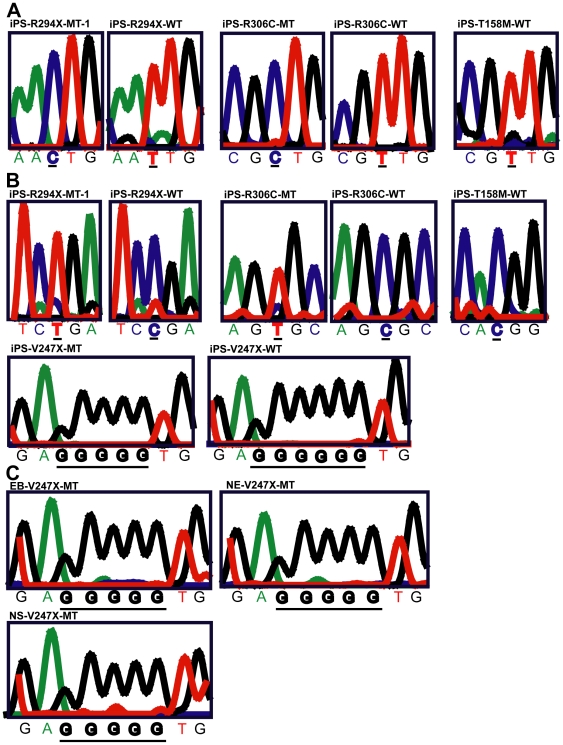
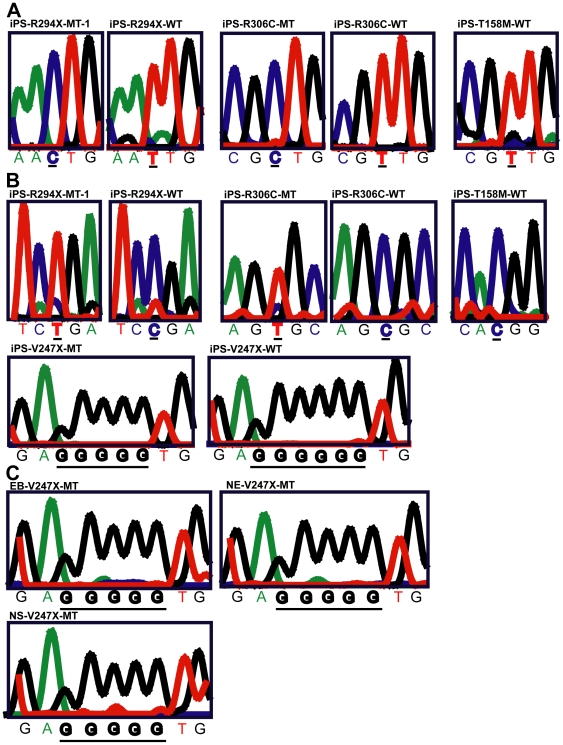
Geriatric syndromes: clinical, research, and policy implications of a core geriatric concept.
Geriatricians have embraced the time period “geriatric syndrome,” utilizing it extensively to focus on the distinctive options of widespread well being circumstances in older folks. Geriatric syndromes, similar to delirium, falls, incontinence, and frailty, are extremely prevalent, multifactorial, and related to substantial morbidity and poor outcomes. Nevertheless, this central geriatric idea has remained poorly outlined. […]